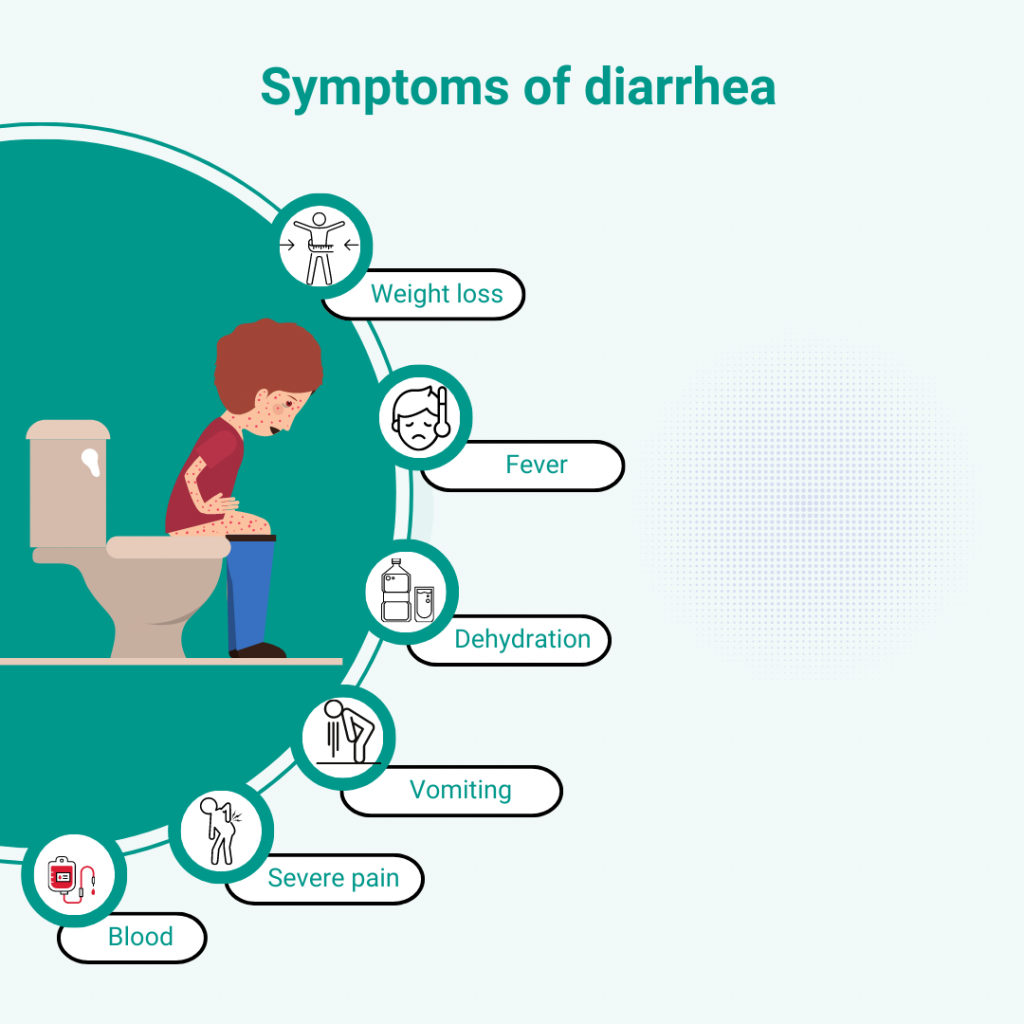
Diarrhea, characterized by frequent, loose, or watery stools, is usually the body’s response to infections, food intolerances, stress, or digestive issues. While it often resolves within a few days, finding immediate relief can make a significant difference. This guide covers effective strategies to stop diarrhea quickly, along with tips for rehydration, managing symptoms, and understanding when to seek medical help.
Nitazoxanide 500 mg is an antiparasitic medication commonly used to treat infections caused by protozoa and helminths. It is effective against conditions such as giardiasis, amoebiasis, and cryptosporidiosis.
Understanding Diarrhea: Causes and Types
Before diving into remedies, it’s important to understand the types of diarrhea and their causes. Diarrhea can be classified into three primary types:
-
Acute Diarrhea: Often caused by viral or bacterial infections, food poisoning, or stress. This type lasts one to two days and generally resolves on its own.
-
Chronic Diarrhea: Lasting over two weeks, chronic diarrhea may indicate an underlying medical condition like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, or other digestive issues.
-
Traveler’s Diarrhea: Typically results from consuming contaminated food or water while traveling in regions with poor sanitation.
Knowing the cause of diarrhea can help determine the best approach to relief and treatment. However, for immediate relief, there are steps you can take to manage and potentially stop symptoms quickly.
Immediate Home Remedies to Stop Diarrhea
1. Stay Hydrated
Diarrhea leads to fluid loss, which can result in dehydration, an especially serious concern for children and older adults. Staying hydrated is essential, as the body loses both water and essential electrolytes. Here’s how to rehydrate effectively:
- Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS): ORS packets, available at pharmacies, contain an ideal balance of salt and sugar to help the body absorb fluids more effectively.
- Homemade Electrolyte Solution: Mix 1 liter of water with 6 teaspoons of sugar and 1/2 teaspoon of salt for a quick rehydration option.
- Coconut Water or Broth: Coconut water and clear broths are good sources of potassium, sodium, and other minerals, helping restore electrolyte balance. Nitazoxanide 200 mg is an antiparasitic medication commonly used to treat infections caused by protozoa and helminths. It is effective against conditions such as giardiasis, amoebiasis, and cryptosporidiosis.
2. Try the BRAT Diet
The BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast) is often recommended for those experiencing diarrhea. These bland, low-fiber foods can help firm up stool and are gentle on the digestive tract. Here’s a breakdown of each food’s benefits:
- Bananas: High in potassium, bananas help replenish lost electrolytes and contain pectin, a fiber that helps solidify stool.
- Rice: Plain white rice is easy to digest and can absorb excess fluid in the intestines.
- Applesauce: Like bananas, apples contain pectin, which helps absorb excess water in the digestive system.
- Toast: Plain toast, without butter or spreads, is a bland carb that can help add bulk to stool.
3. Avoid Certain Foods and Drinks
While experiencing diarrhea, avoid foods and beverages that could exacerbate symptoms. Key items to avoid include:
- Dairy: Lactose, found in dairy products, can irritate the digestive tract during bouts of diarrhea, especially in those with lactose intolerance.
- High-Fiber Foods: Avoid raw fruits and vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, as they can make stools more watery.
- Spicy and Fatty Foods: These can further irritate the stomach and intestines, prolonging symptoms.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can increase dehydration and may stimulate bowel movements, worsening diarrhea.
4. Over-the-Counter Medications
Certain over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide quick relief from diarrhea by slowing bowel movements or absorbing excess water in the intestines. However, consult a doctor before using these if you have a severe or chronic condition, as these medications may not be appropriate in all cases.
- Loperamide (Imodium): Loperamide is an anti-diarrheal medication that reduces the frequency of bowel movements, often providing relief within a few hours.
- Bismuth Subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol): This medication not only helps stop diarrhea but also soothes the stomach and reduces gas, nausea, and cramps.
Note: Avoid OTC anti-diarrheal medications if diarrhea is caused by a bacterial infection, as stopping the bowel movements could trap bacteria in the intestines. Consult a healthcare provider in cases of fever, severe abdominal pain, or if diarrhea persists.
5. Probiotics for Gut Health
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health and can help restore balance in the digestive system, especially after an infection or antibiotic use. They may not provide immediate relief but can shorten the duration of symptoms and help prevent future episodes.
- Yogurt and Kefir: These contain natural probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, which can help replenish the gut’s healthy bacteria.
- Probiotic Supplements: Available in capsule or powder form, probiotics like Saccharomyces boulardii are often recommended for diarrhea relief.
6. Herbal Teas for Soothing Effects
Certain herbal teas can be soothing to the digestive tract and help alleviate symptoms:
- Ginger Tea: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger tea can help reduce inflammation in the gut and reduce nausea.
- Chamomile Tea: Chamomile has antispasmodic properties, which may reduce cramping and relax the intestines.
- Peppermint Tea: Peppermint has a calming effect on the digestive tract and may ease bloating and gas associated with diarrhea.
7. Get Plenty of Rest
Diarrhea can be exhausting, and getting enough rest helps your body recover faster. Avoid strenuous activities and give your body time to heal, as physical exertion can worsen dehydration and fatigue.
When to Seek Medical Help
While most cases of diarrhea resolve within a few days with home care, certain signs may indicate a more serious issue. Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Diarrhea lasting more than two days for adults or 24 hours for children
- Severe abdominal or rectal pain
- A high fever (above 102°F)
- Blood or mucus in stools
- Signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, dizziness, or reduced urination
- Diarrhea accompanied by vomiting that prevents fluid intake
Preventing Future Episodes of Diarrhea
Prevention is key to avoiding recurrent episodes. Here are some simple tips to help prevent diarrhea in the future:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom and before meals. Proper hygiene helps prevent the spread of infectious agents that can cause diarrhea.
- Be Cautious When Traveling: Avoid street food and drink bottled or boiled water in areas with poor sanitation to reduce the risk of traveler’s diarrhea.
- Limit Triggers: Identify and avoid any food or drink triggers that consistently lead to digestive discomfort or diarrhea.
- Consider Probiotics: Regular use of probiotics may help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, especially after taking antibiotics, which can sometimes lead to diarrhea.
Conclusion
Diarrhea can be disruptive, but with the right approaches, relief can often be found quickly. Staying hydrated, following the BRAT diet, avoiding irritants, and using over-the-counter medications (when appropriate) are effective ways to manage symptoms. While these remedies can provide fast relief, always consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist, worsen, or are accompanied by other concerning signs. Taking preventative steps, such as practicing good hygiene and being cautious with dietary choices, can also help reduce the likelihood of future episodes.