Introduction
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) affects millions worldwide, making it challenging to breathe and leading to other health complications. While medical treatments and lifestyle changes are essential for managing COPD, diet also plays a crucial role. Proper nutrition can help reduce inflammation, support lung function, and improve overall well-being, allowing those with COPD to manage symptoms more effectively. We’ll discuss the foods that support respiratory health and provide dietary strategies for individuals with COPD.
Definition
The chronic inflammatory lung illness known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) makes it difficult for air to leave the lungs. Coughing, wheezing, mucus production, and trouble breathing are some of the symptoms of COPD.
Understanding COPD and the Role of Diet
COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by breathing difficulties, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. For people with COPD, breathing requires more energy than it does for those with healthy lungs, which means their bodies often require additional calories. Eating a balanced diet can help support this increased energy demand while promoting respiratory health and reducing the risk of infection, which is especially important since lung infections can exacerbate COPD symptoms.
Why Diet Matters in COPD Management
-
Energy: COPD can increase calorie needs due to the effort required to breathe. Eating nutrient-dense foods helps maintain energy levels.
-
Inflammation: Inflammation may be lowered or increased by specific meals. Managing inflammation is critical in COPD, as lung inflammation can worsen symptoms.
-
Immune Support: A strong immune system helps reduce the risk of respiratory infections, a common complication of COPD.
Key Nutrients for COPD Management
Antioxidants:
Antioxidants play an essential role in protecting the lungs from oxidative stress, which can worsen inflammation. Vitamins C, E, and beta-carotene are potent antioxidants that help protect lung tissue.
Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries, vitamin C helps protect against lung infections and supports immune health.
Vitamin E: Nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are some sources. Vitamin E supports lung function and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Beta-carotene: Present in carrots, sweet potatoes, and apricots, beta-carotene can help reduce inflammation in the respiratory system.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3s, found in fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines), walnuts, and flaxseeds, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They help reduce lung inflammation and may support overall lung function in people with COPD.
Protein:
Protein is essential for muscle maintenance, which is especially important for people with COPD since respiratory muscles are constantly engaged. High-quality protein sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and legumes.
Magnesium:
Magnesium helps relax the muscles involved in breathing, making it an essential mineral for those with respiratory conditions. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts, seeds and whole grains.
Fiber:
A diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall digestive health and can help manage weight, which is important as being overweight or underweight can affect COPD symptoms.
Foods That Support Respiratory Health
Now that we’ve covered the essential nutrients, let’s look at specific foods that can benefit individuals with COPD.
1. Fatty Fish
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation in the lungs and improve lung function. Regularly including fatty fish in your diet can also help reduce the risk of COPD flare-ups.
2. Leafy Green Vegetables
Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with magnesium, fiber, and antioxidants, making them beneficial for lung health. These greens help relax lung muscles and support overall lung function, which is particularly helpful for people with COPD.
3. Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are high in vitamin C, an antioxidant that supports immune function and reduces inflammation. Consuming citrus fruits can lower the risk of respiratory infections, which can worsen COPD symptoms.
4. Berries
Berries like strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants, specifically vitamin C and flavonoids, which help reduce inflammation and support lung health. Their high fiber content also promotes digestive health, which is beneficial for overall well-being.
5. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are high in magnesium, vitamin E, and healthy fats. These nutrients help reduce inflammation, improve lung function, and support respiratory muscle function. Including a variety of nuts and seeds can enhance your diet’s nutritional profile.
6. Apples
Apples contain high levels of antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which help protect the lungs from oxidative damage. Regular apple consumption has been associated with better lung function in people with respiratory conditions.
7. Garlic and Onions
Garlic and onions are rich in anti-inflammatory compounds that may help reduce mucus production and ease breathing. They contain allicin, an antioxidant that helps combat lung infections and reduces inflammation in the respiratory tract.
8. Whole Grains
Whole grains, such as oats, brown rice, and whole wheat, provide fiber, which supports digestive health and helps maintain a healthy weight. Whole grains also help stabilize blood sugar, which can prevent energy crashes that make breathing more difficult for people with COPD.
9. Carrots and Sweet Potatoes
Carrots and sweet potatoes are high in beta-carotene, an antioxidant that the body converts into vitamin A. This nutrient helps maintain healthy lung tissue and supports immune health.
10. Beans and Legumes
Plant-based sources of fibre and protein include beans, lentils, and chickpeas. They help maintain muscle strength, support immune function, and stabilize energy levels, making them an excellent choice for people with COPD.
Foods to Avoid
While some foods support respiratory health, others can worsen COPD symptoms. Here are some foods that people with COPD should consider limiting:
-
Processed Foods: These often contain high levels of sodium, which can lead to fluid retention and make breathing more difficult.
-
Fried Foods: Fried foods can cause bloating, making it harder for people with COPD to breathe.
-
Carbonated Beverages: Carbonated drinks can increase bloating and put pressure on the diaphragm, making breathing more challenging.
-
Excessive Dairy Products: Some individuals find that dairy products increase mucus production, which can worsen COPD symptoms. However, this varies from person to person.
-
Sugary Foods: High-sugar foods can cause weight gain and may increase inflammation, exacerbating COPD symptoms.
Practical Tips for Eating with COPD
Smaller, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent bloating and provide a steady source of energy.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps thin mucus, making it easier to breathe. Aim for at least eight cups of water daily unless otherwise advised by your healthcare provider.
Prepare Healthy Snacks: Keep snacks like fruits, nuts, and vegetables readily available to meet your body’s energy needs without feeling overly full.
Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: Choose nutrient-dense foods over empty-calorie foods to meet the increased calorie demands of COPD while maximizing nutrition.
Monitor Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing COPD symptoms. Underweight individuals should consume calorie-dense, nutritious foods, while those who are overweight may benefit from a balanced, low-calorie diet to avoid placing extra strain on the lungs.
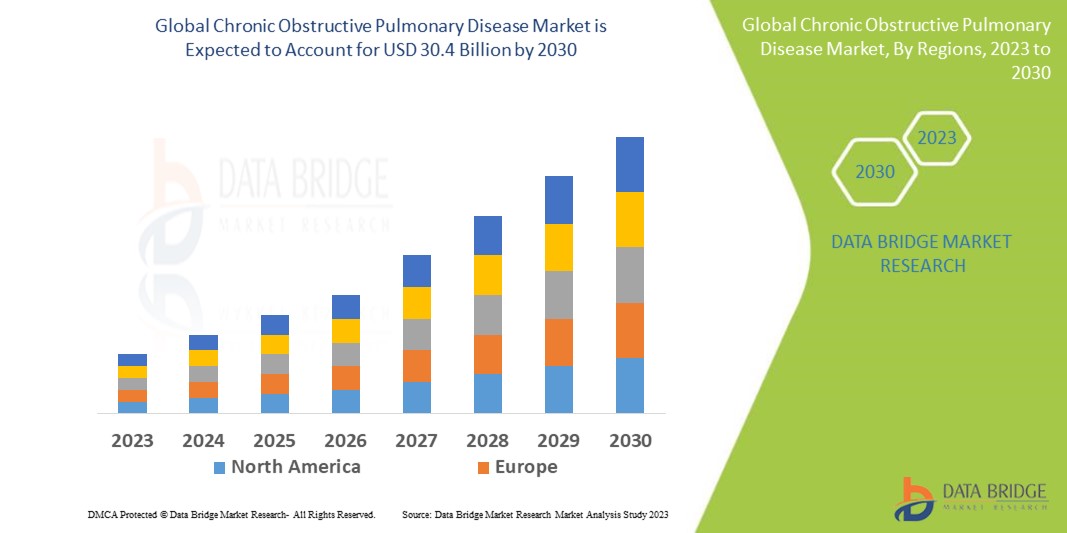
Growth Rate Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global market for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which was valued at USD 19.8 billion in 2022, is projected to jump to USD 30.4 billion by 2030 and see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% from 2023 to 2030.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-market
Conclusion
For people with COPD, a diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, protein, and magnesium can play a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving respiratory health. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and citrus fruits, individuals with COPD can reduce inflammation, support lung function, and boost immunity. Additionally, avoiding processed foods, fried foods, and excessive dairy can help prevent exacerbation of COPD symptoms. Making these dietary adjustments, alongside medical treatments and lifestyle changes, can empower those with COPD to live a healthier, more comfortable life.